I packaged the latest development version of jOWL into a 0.5 release, available at Google Code. jOWL is an AJAX/javascript extension to jQuery that I am developing. The jOWL library parses and reasons with OWL-DL documents. Supported browsers for this release are Internet Explorer 7 and Firefox 2 & 3.
This release is accompanied by several new and impressive demo's (in my humble opinion). These make use of the new functionalities that have been incorporated so far. Below are some important highlights.
Reasoning over Individuals: Demo 2: jOWL integration with Simile Exhibit
Simile Exhibit is an MIT project that allows complex data visualisations to be defined entirely on the client-side (javascripted). This means no server-side scripting is needed (no PHP, Ruby, JSP, ASP, ...) and no database access is required. In Exhibit, data is defined in a rich, but flat, JSON format.
The jOWL library is designed with similar ideas and goals in mind, but focuses on OWL semantics and vertical search instead. So on the one hand jOWL takes into account subsumption/inheritance, but on the other hand Exhibit has powerful visualisations. I believed it would be an interesting experiment to try and reconcile the two. The results of this labor can be seen at the jOWL - Exhibit demo page that has been set up. jOWL loads the OWL file, grabs all instances of the specified class (wine), grabs all restrictions (relations) applicable for these, and converts this into a JSON data format that Exhibit can read. Exhibit then takes care of the further visualisations and filtering.
The Exhibit results also hook back to some jOWL functionality, which allows visualisation of a little more supporting information. Clicking on Meursault in the below example (image) shows the ontological classification of this type of wine.
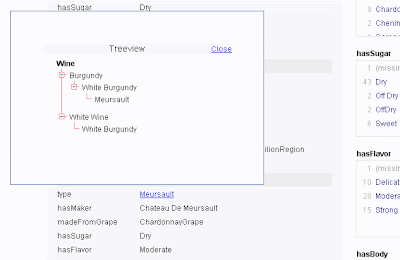
Ontology Browsing
One item on my todo list was to expand the tests and demo's to include more diverse types of OWL-DL files. Even though OWL-DL is a standard, there are alternative ways to express things. In general, ontology elements are uniquely referenced by the attribute 'rdf:ID'. It is however also possible to use external declarations only, by means of the 'rdf:about' attribute and external URI's. This has some particular benefits, most importantly the identity of the ontology elements always points to one and the same location, no matter the location of the OWL file, and therefore is common practice in building ontologies. The external URI should then declare the ontology elements as well at the specified location, but funnily enough this is often overseen. Previously jOWL only indexed elements referenced by 'rdf:ID', but this has now been expanded to also include elements only referenced through 'rdf:about'. The concrete result of this rewrite is that ontologies like the Basic Formal Ontology or the Ontology of Biomedical Investigations can now also be properly visualised with jOWL.
Another change is that the foundations for a new User Interface component are being drafted. This new component is meant to visualise descriptions, labels, disjoints, outgoing non-hierarchical relations, etc... The prototype (under development) can be seen for example in the BFO (Basic Formal Ontology) demo. Hand in hand with this component is the ability to use permalinks, links that allow you to externally reference a given owl:Class. Examples of the permalink functionality is also visible in that demo.
Documentation, and visualisation of RDFa embedded OWL syntax
Documentation was somewhat lacking in the past, but I put in an effort to create it. And even more, jOWL is used to visualize it. Initially I defined the documentation in an OWL-DL file. I kept that, now outdated, owl file accessible, because it demonstrates how to include HTML syntax in rdfs:comments (by wrapping in CDATA tags). But I decided to take another approach in the end with this documentation. Instead of loading an OWL-DL file, all the documentation resides in an html file, which is enriched with RDFa markup. The RDFa indicates which ontology classes exist, along with their descriptions ('rdfs:comments') and more. jOWL then extracts an OWL-DL file directly from this RDFa-enriched html page, and adapts the page to visualize it the jOWL way instead. Basically this is a real application to what I previously wrote in the blog post 'Embedding OWL syntax in HTML with RDFa'.
Some people may have doubts on this approach, and I must admit I haven't entirely made my mind up on the applicability of it as well. For one it is only suitable if the OWL syntax remains simple, as for example in the case of documentation, where hierarchical information (vertical representation of data) is enough. But it does come with some major advantages:
- A big plus, just being practical: Content is accessible to search engine spiders and people who disable javascript. Ergo it solves the search engine access issues always seen with any other AJAX implementation.
- It is much simpler & userfriendly than writing an OWL-DL file. Still requires some effort. But (in combination with jOWL) it seriously lowers adoption barrier for using OWL.
- The flat representation of the documentation is hidden, and instead you the user is presented with a more dynamic/intelligent view on that data.
And finally: The link to this documentation, which serves as a demo on it's own.
Hope you enjoy the new demo's,
David.